Ear Echo: Why Your Voice Sounds Louder in Your Ears—and What You Can Do About It
If you’ve ever spoken, breathed, or chewed and thought, “Why does everything sound so loud inside my head?” you may be experiencing what many people casually call ear echo.
This internal echoing sensation is medically known as autophony, a symptom that can make your voice, footsteps, or even your own breathing sound amplified and unnatural.
While the experience can feel strange or even alarming, ear echo is more common than you might think—and in many cases, it’s very treatable. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the most likely causes, the symptoms to look for, and the steps you can take to find relief.

What Is “Ear Echo”?
“Ear echo” refers to the sensation of hearing sounds—especially your own voice—more loudly or resonantly inside your ear.
People often describe it as:
- Hearing their voice loudly “booming” inside the ear
- Breathing that sounds like wind rushing through a tunnel
- Hearing footsteps echo through their head
- A feeling of being “too aware” of internal sounds
This phenomenon is typically connected to conditions that affect the middle ear, the Eustachian tube, or the way sound travels through the ear canal.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, autophony occurs when your voice or internal sounds bypass the usual sound pathways and directly vibrate the eardrum or middle-ear structures, creating an internal echo effect.

Common Causes of Ear Echo (Autophony)
Ear echo is often linked to a condition involving the Eustachian tube—the canal that helps equalize pressure between your middle ear and the outside world.
Here are some of the most common culprits:
1. Patulous Eustachian Tube (PET)
Patulous Eustachian Tube occurs when the Eustachian tube stays abnormally open, allowing sound vibrations to travel in ways they shouldn’t.
Symptoms often include:
- Hearing your own voice very loudly
- Hearing your breathing inside your ear
- A sensation of fullness or distortion
PET is one of the most common medical causes of autophony.
2. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) occurs when the tube becomes blocked or swollen, often due to allergies, colds, or sinus issues.
This can cause:
- Muffled hearing
- Pressure changes
- Occasional echo-like sensations
When pressure can’t equalize properly, sound may feel distorted, muted, or reverberant.
3. Middle Ear Fluid
Fluid buildup—often from allergies or infections—can create an internal echo, making your voice sound like it’s reverberating inside your ear. Children experience this frequently, but adults can as well.
4. Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome (SCDS)
Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome (SCDS) is a rarer cause of ear echo. It occurs when a thin bone layer in the inner ear develops an opening.
People with SCDS may experience:
- Autophony
- Hearing eye movements (yes, really)
- Balance disturbances
- Heightened perception of internal sounds
Other Symptoms That May Accompany Ear Echo
If you’re experiencing ear echo, you might notice additional symptoms, including:
- A feeling of fullness or “hollowness” in the ear
- Fluctuating hearing
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing)
- Sensitivity to internal noises
- Occasional dizziness or imbalance
- Muffled or distorted external sounds
If ear echo appears suddenly—especially with hearing loss—seek care right away. Sudden hearing changes may be considered a medical emergency.
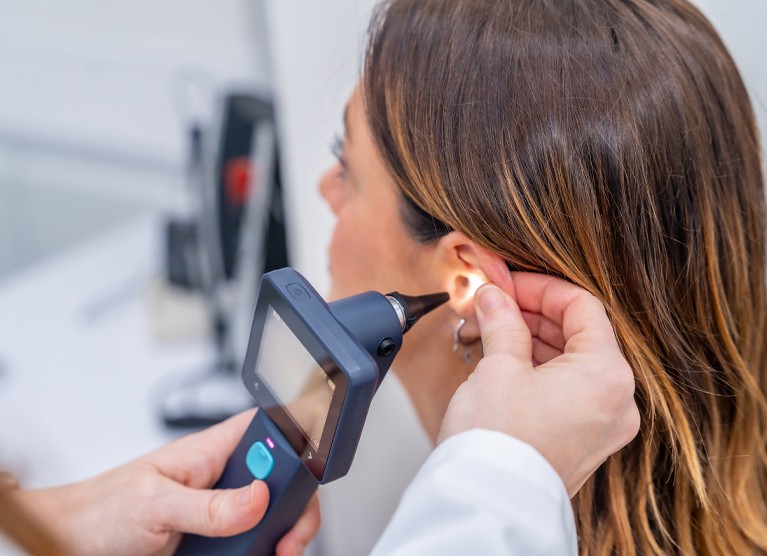
How Ear Echo Is Diagnosed
A hearing care professional (HCP) will typically perform:
- A comprehensive hearing screening
- A middle-ear assessment to check pressure and eardrum mobility
- A review of your medical history, symptoms, and triggers
- Additional specialized testing if SCDS or PET is suspected
In some cases, you may be referred to an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist for further evaluation and imaging.
Treatment Options for Ear Echo
The right treatment depends on the underlying cause. Common approaches include:
For Patulous Eustachian Tube (PET)
- Improving hydration
- Nasal sprays or drops prescribed by a physician
- Avoiding caffeine and decongestants (which can worsen symptoms)
- In rare or severe cases, surgery
For Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
- Allergy management (medications or environmental control)
- Decongestants (only as advised by your doctor)
- Steam inhalation or nasal saline rinses
- Ear pressure equalizing exercises (e.g., swallowing, gentle Valsalva maneuver as advised)
- Treatment for sinus infections if present
For Middle Ear Fluid
- Watchful waiting (fluid often resolves on its own)
- Medical treatment for ear or sinus infections
- In more severe or persistent cases, drainage or ear tubes (as decided by an ENT)
For Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome (SCDS)
Treatment for SCDS typically requires an ENT specialist and may include:
- Monitoring mild cases
- Surgical repair in more severe cases affecting balance and quality of life

How Hearing Aids Can Help With Echo or Distorted Sound
If your ear echo is connected to underlying hearing loss, modern hearing aids may help improve how sound is processed and delivered to the ear.
Benefits can include:
- More natural perception of your own voice
- Reduced internal distortion or “booming” sensation
- Clearer overall hearing in everyday environments
If hearing loss is part of the picture, an HCP can recommend whether hearing aids or other technology might improve comfort and clarity.

When to See a Hearing Care Professional
You should schedule a hearing evaluation if:
- Ear echo persists for more than a week
- Symptoms worsen when speaking, chewing, or breathing
- You experience hearing loss or muffled sound
- The echo sensation is accompanied by dizziness, pressure, or pain
- Your symptoms interfere with work, conversations, or daily activities
If you suddenly lose hearing, seek urgent medical attention immediately.
A Beltone hearing care professional can help determine the cause of your symptoms and offer appropriate next steps—whether that includes hearing testing, management strategies, or a referral to an ENT specialist.
Take the Next Step Toward Relief
Ear echo can be frustrating and disruptive—but it’s also often treatable. With the right support, you can regain comfort and clarity in your hearing.
Schedule a free hearing screening* with your local Beltone today to better understand what’s causing your symptoms and explore personalized solutions.

Online Hearing Test


